Did you ever think about how your favorite animated movies and video games are created? All done with well structured process known as the 3D animation pipeline. From ideas to finished scenes, every studio follows 3D animation workflow to ensure quality, speed, and consistency. It is an essential framework that simplifies animation production process and ensures that all stages from pre-production to post-production are carried out properly.
This blog helps you understand 3D animation process step by step, how 3D animation production pipeline works in real studios, what happens at each stage, and which tools are used.
What is 3D Animation Pipeline?
3D animation pipeline is well structured 3D animation workflow that simplifies complex process of creating 3D content into manageable and sequential stages. It is step by step process that helps studios make quality animation on time. It’s divided into three main phases: pre‑production, production, and post‑production.
Difference Between 3D Animation Process and 3D Animation Production Pipeline
3D animation process and 3D animation production pipeline, both terms are used interchangeably but there is a difference.
3D animation process refers to creative journey of making animation including all artistic and technical decisions. On the other hand, 3D animation production pipeline is systematic structured framework that studios follow to organise 3D animation process. The process of 3D animation is like cooking a meal and 3D animation pipeline is recipe with exact step by step guide.
Why Studios Follow Pipeline Based Workflow
When studios work on large scale animation projects, it requires many artists at different stages of 3D animation production, so they required structure animation pipeline to create final asset without missing deadlines. Studios rely on proper 3D animation workflow because it:
- saves both time and budget
- Avoid rework and errors
- Allow team to work simultaneously
- Also give clear quality checkpoints at each production phase.
Complete Overview of the 3D Animation Production Pipeline
3D animation production pipeline is divided into three main stages:
- Pre-production
- Production
- Post-production
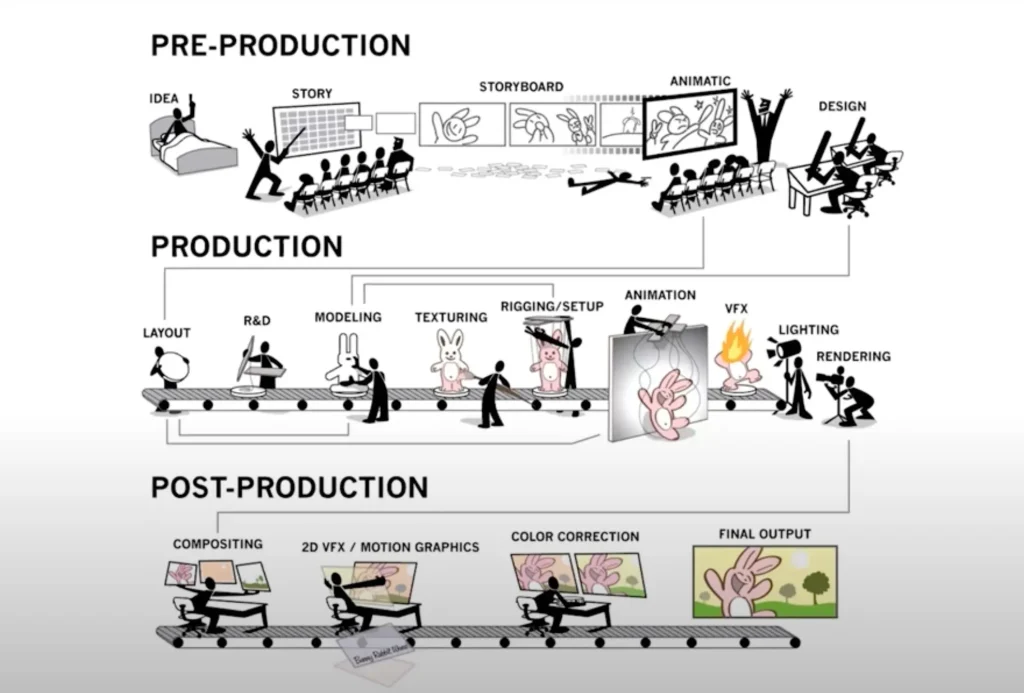
Stage 1:
What is pre-production in animation pipeline?
Pre-production in animation pipeline involves all planning activities including conceptualization, scriptwriting, storyboarding, and design development. This phase establishes creative vision and technical requirements before any 3D work begins.
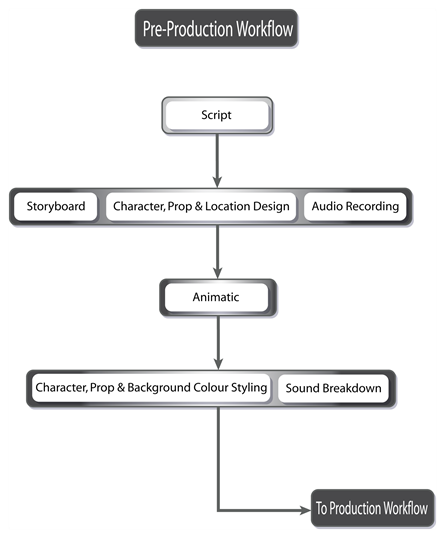
Pre-production include following steps:
1. Concept Development and Idea Generation
As you know every great animation starts with solid and thoughtful idea. So to start 3D animation project, well thought idea is necessary. In this first stage, creators outline story ideas, theme and message that they want to convey to audience. Teams usually put together mood boards, reference materials, and visual ideas to help guide the look and style during production.
2. Scriptwriting and Storyboarding
Storyboard guide entire 3D animation workflow that helps animators to understand timing, camera angles and scene flow. Scriptwriting is formal written version of story which includes characters movements, environment, their dialogue, actions and time.
3. Animatic
Animatic is moving version of storyboard. This is rough draft that shows how the project will flow, using simple 2D drawings to display the timing and sequence of scenes. Over time, this animatic develops into the final edit of the project.
4. Design
This stage include final look of project. It shows concept of story, character design, character costume, and environment.
Stage 2:
What is 3D Animation Production Process?
The production stage is where all the planning finally turns into action. In this stage, the right team and artists take the visual parts of 3D animation and work on them. Team leaders make sure the work stays on schedule and meets the quality set during pre-production. The results from this stage decide how the whole 3D animation will look.
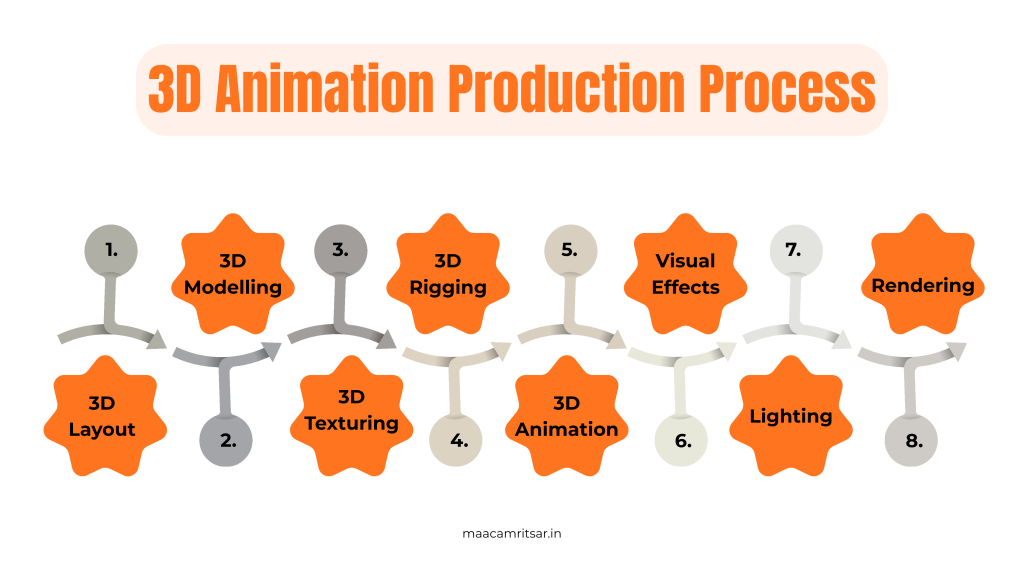
3D animation production process includes:
1. 3D Layout
We call 3D layout the 3D version of 2D animatic. It contains 3D attributes such as shape, size, characters, and environment. It is like backbone of animation production process which transforms storyboard into 3D action plan and guides entire animation process.
2. 3D Modelling
In 3D animation pipeline, 3D modelling is stage where artists build digital characters, props and environments with specialized 3D software such as Maya and 3D Max.
3. 3D Texturing
3D texturing is the process of adding surface details to 3D models so they look realistic. The 3D texturing is the art of dressing up 3D models with colors, materials, and details so they look real and engaging in the final animation.
4. 3D Rigging
3D rigging is art of building the skeleton and controls inside 3D model so animators can make it move naturally. For example–
Imagine a puppet, puppet body is 3D model, its strings and joints are rig. Puppeteer is the animator, without strings (rigging), the puppet can not move.
5. 3D Animation
In 3D animation, artists bring digital characters, props, and environments to life through movement. After modeling, texturing, and rigging, animators use the rigged models to create actions, emotions, and storytelling moments.
- It turns rigged models into dynamic performances.
- 3D animation conveys emotion, personality, and narrative to support storytelling.
Without animation, the project would remain only series of still images.
6. Visual Effects (VFX)
VFX in the animation pipeline is the stage where digital effects like fire, water, explosions, and magic are created and making the final animation more dynamic, immersive, and visually stunning.
- Visual effects highlight dramatic moments in animation and support storytelling.
- VFX artists work closely with animators, lighting, and compositors to ensure effects blend naturally.
7. Lighting
Lighting is the stage where artists set up virtual lights in 3D scene to control how everything looks. Just like in filmmaking, lighting defines mood, depth, and realism. It makes characters, props, and environments feel alive and visually appealing.
8. Rendering
In the final step of the 3D animation pipeline, the computer processes models, textures, lighting, animation, and VFX to produce the finished output.
- Rendering ensures the animation looks complete and professional.
- Combines work from modeling, rigging, animation, texturing, lighting, and VFX.
- Rendered frames are sent for editing, compositing, and sound integration.
Stage 3:
What is animation post production process?
Post production process is last stage in which final touch ups are added to project to make it look polished and professional.
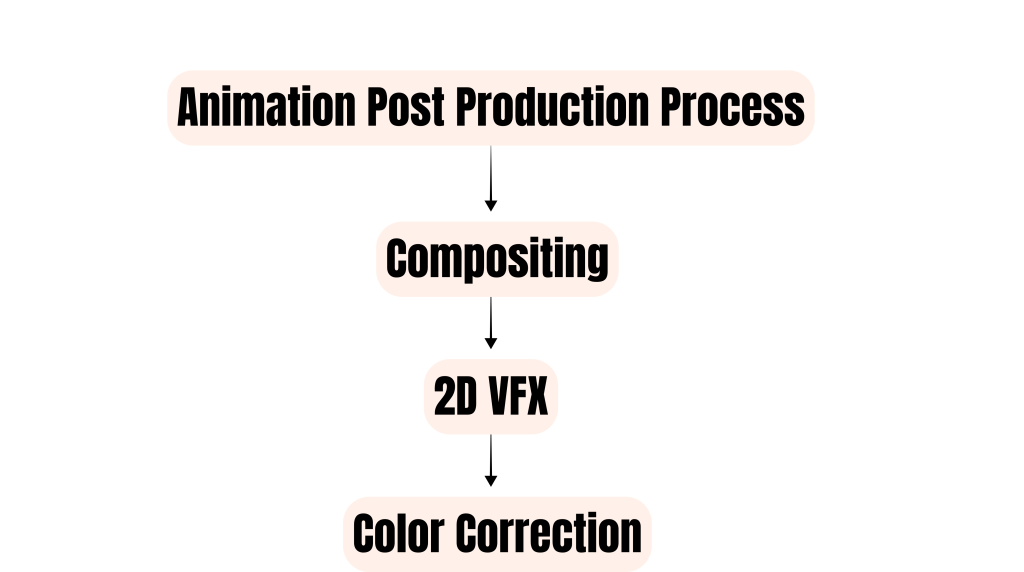
This stage includes:
1. Compositing
Compositing is the process of combining all the visual elements of scene such as characters, backgrounds, effects, and lighting into one final sequence. It is like layering pieces of art together so they look seamless and polished.
2. 2D VFX
2D VFX in post-production are visual enhancements like overlays, motion graphics, and effects applied in 2D space to polish and stylize the final animation.
3. Color Correction
Color correction is the process of adjusting and balancing colors in the final animation so everything looks consistent, natural, and visually appealing. Artists ensure that shots match each other in tone, brightness, and contrast, regardless of how they were originally rendered.
Common 3D Animation Software Used Across the Pipeline
3D animation software options range from beginner to studio level tools:
| Beginner to intermediate: | 1. Blender offers complete free pipeline solution 2. Cinema 4D provides intuitive motion graphics and animation tools 3. iClone specializes in quick character animation |
| Professional studio level | 1. Autodesk Maya dominates character animation and rigging 2. Houdini excels at procedural modeling and effects 3. Nuke leads compositing workflows 4. ZBrush sets the standard for digital sculpting 5. Substance Suite handles texturing across productions |
Conclusion
3D animation pipeline is foundation of animation production. Each stage from pre production to post production, every stage is very important to deliver high quality visuals. When teams follow this animation pipeline properly, they work faster, avoid mistakes, and produce high-quality animation. It not only improves skills but also prepares you for real studio workflows used in the animation industry today and in the future.
FAQ’s for 3D Animation Pipeline
Q1. What is the 3D animation pipeline in simple terms?
Ans. In simple words 3D animation pipeline is step by step process used to create animation. It starts with planning and design, then moves to modeling, animation, lighting, rendering, and ends with final editing. It helps teams work smoothly and avoid confusion.
Q2. What is the difference between 3D animation and CGI pipeline?
Ans. 3D animation pipeline focuses on animated characters and scenes. CGI pipeline is broader, it also includes visual effects, simulations, and realistic elements added to live action footage.
Q3. Why do we use pipeline for 3D animation production?
Ans. With the help of structured pipeline the work is organized. It saves time, reduces mistakes, improves quality, and allows multiple artists to work together efficiently on the same project.
Q4. How do you make a strong animation portfolio?
Ans. Strong animation portfolio shows your best work, not all your work. Focus on quality, clear animation skills, good storytelling, and short demo reels. Use simple presentations and keep updating them regularly.


Leave a Reply